Procurement and purchasing are often used interchangeably, yet they serve different roles within the procurement process. Understanding how these two functions interact helps organisations optimise procurement effectiveness, control costs, and build strategic supplier relationships.
What is Purchasing?
Purchasing focuses on short-term, transactional activities such as placing orders, receiving goods, and strong price comparison. It’s primarily cost-driven, emphasising immediate savings per transaction.
The Steps of a Purchasing Process
- Order Placement
Issue Purchase Orders based on purchases made. This involves creating accurate and detailed orders to ensure suppliers understand and deliver as per the requirements. - Order Expediting
Ensure timely delivery by tracking orders. This step involves regular communication with suppliers to monitor progress and address any potential delays. - Receiving Goods/Services
Accept and inspect the delivered items. Verification against purchase orders ensures that the correct items are received in the right condition. - Payment Processing
Process invoices and facilitate payments to suppliers. Accurate and timely payments maintain good supplier relationships and ensure compliance with contractual terms.
What is a Procurement Process?
Procurement is a broader and more strategic process. It involves sourcing for vendors, negotiating contracts, managing supplier relationships, and ensuring compliance. Apart from focusing on pricing, the procurement process considers overall value, risk mitigation, and long-term business objectives.
The Steps of a Procurement Process
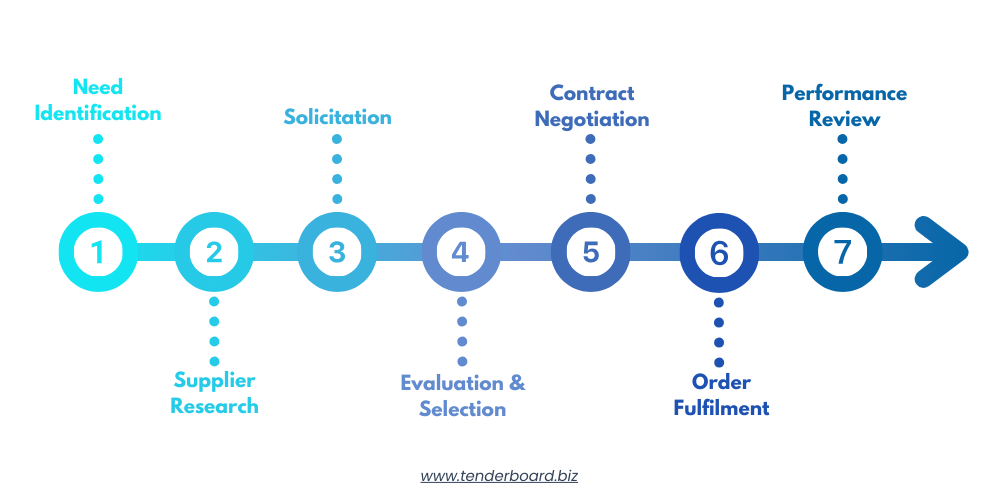
- Needs Identification
Determine the specific goods or services are required to meet organisational objectives. This involves collaborating with various departments to understand their needs and forecasting future requirements. - Supplier Research
Identify potential suppliers and assess their capabilities. This step includes market analysis, evaluating supplier reliability, financial stability, and alignment with the organisation’s values and standards. - Solicitation
Request proposals or quotations from selected suppliers. This involves preparing and issuing Request for Proposals (RFPs) or Request for Quotations (RFQs), ensuring clarity in specifications and expectations. - Evaluation and Selection
Analyse supplier proposals and select the most suitable option. Evaluation criteria may include cost, quality, delivery timelines, and supplier reputation. - Contract Negotiation
Negotiate terms and conditions to establish a formal agreement. This step ensures that both parties agree on pricing, delivery schedules, quality standards, and other pertinent details. - Order Fulfilment
Oversee the delivery of goods or services as per the contract. This includes monitoring production, ensuring compliance with specifications, and coordinating logistics. - Performance Review
Monitor supplier performance and manage relationships for future engagements. Regular assessments help in identifying areas for improvement and fostering long-term partnerships.
How Procurement and Purchasing Fit into the Procurement Process
Both functions are interconnected and crucial to an overall, well-structured procurement process. Procurement ensures that purchasing activities align with organisational goals, while purchasing guarantees that strategic sourcing efforts materialise into tangible goods and services.
The procurement process can be divided into distinct stages, where procurement and purchasing collaborate to ensure efficiency and compliance.
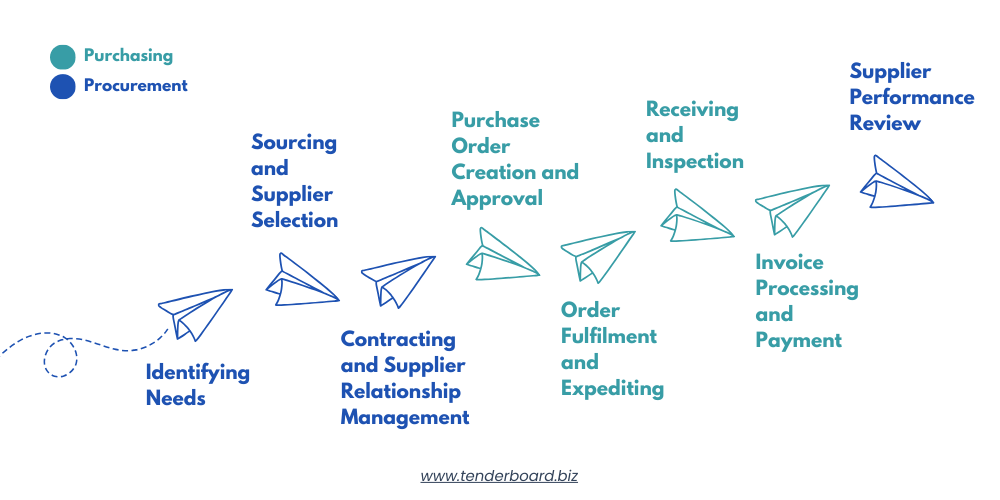
- Identifying Needs (Procurement)
Procurement starts with assessing needs which includes engaging stakeholders, analysing past usage, and forecasting demand. The goal is to align procurement with business objectives and cost efficiency - Sourcing and Supplier Selection (Procurement)
Procurement teams evaluates suppliers based on cost, quality, reliability, and sustainability through RFPs, RFQs, and negotiations. Supplier selection determines the vendors with whom the organisation will establish relationships. - Contracting and Supplier Relationship Management (Procurement)
After selecting suppliers, procurement teams formalise agreements through contracts covering terms, pricing, and compliance. Procurement also manages supplier relationships to ensure consistent quality and mitigate risks. - Purchase Order Creation and Approval (Purchasing)
With contracts in place, Procurement teams issue purchase orders (POs) which confirm quantities, pricing, and delivery. Approval workflows ensure compliance with procurement policies. - Order Fulfilment and Expediting (Purchasing)
Purchasing teams track orders, ensure timely deliveries, and work with suppliers to resolve any delay issues. - Receiving and Inspection (Purchasing)
When goods or services arrive, purchasing ensures they meet quality and specification requirements. If discrepancies are found, they coordinate with procurement and suppliers to resolve issues. - Invoice Processing and Payment (Purchasing)
Purchasing processes invoices, ensuring they align with purchase orders and contracts. Payments are made based on agreed terms, maintaining supplier trust and avoiding financial penalties. - Supplier Performance Review (Procurement)
Procurement evaluates suppliers using KPIs. Data from purchasing activities, such as order accuracy and on-time delivery rates, contribute to these evaluations. Strong performers earn trust while poor ones may be replaced.
Recognising how procurement and purchasing work together allows organisations to streamline operations and improve efficiency. Some key benefits include:
- Enhanced Cost Management: Procurement negotiates favourable terms, while purchasing ensures adherence to agreed pricing and avoids unnecessary expenditures.
- Stronger Supplier Relationships: Procurement manages long-term partnerships, while purchasing ensures smooth day-to-day transactions.
- Improved Compliance and Risk Management: Procurement establishes policies, and purchasing enforces them to prevent fraud and contractual violations.
- Operational Efficiency: A clear division of responsibilities prevents bottlenecks and ensures smooth procurement cycles.
Digitalise and automate your procurement with eProcurement Platforms
Upgrading from traditional purchasing to a strategic procurement approach benefits business operations and takes your spend management to the next level. TenderBoard’s eProcurement platform simplifies the entire procurement cycle by digitalising and automating your source-to-pay or source-to-contract processes, guiding your staff through compliant procurement workflows and providing your organisation with a buying peace of mind.
Learn how TenderBoard can help you simplify and enhance your procurement processes here – https://www.tenderboard.biz/eprocurement/